Wednesday, December 29, 2010
IPTables Tutorial From Linux Journal
Mastering IPTables Part 1
Firewall Script Part 1
### Start Of Script ###
#!/bin/sh
IPT=/sbin/iptables
$IPT -F
#policies
$IPT -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -P INPUT DROP
$IPT -P FORWARD DROP
#allowed inputs
$IPT -A INPUT --in-interface lo -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
#allow responses
$IPT -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
### End Of Script ###
Mastering IPTables Part 2
Firewall Script Part 2
### Start Of Script ###
#!/bin/sh
IPT=/sbin/iptables
$IPT -F
#policies
$IPT -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -P INPUT DROP
$IPT -P FORWARD DROP
$IPT -t nat -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P PREROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P POSTROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -N SERVICES
#allowed inputs
$IPT -A INPUT --in-interface lo -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A INPUT -j SERVICES
#allow responses
$IPT -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
#allow services
$IPT -A SERVICES -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -m iprange --src-range 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 -p tcp --dport 631 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -m iprange --src-range 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 -p udp --dport 631 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
$IPT -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
### End Of Script ###
Mastering IPTables Part 3
Firewall Script Part 3
### Start Of Script ###
#!/bin/sh
IPT=/sbin/iptables
$IPT -F
#policies
$IPT -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -P INPUT DROP
$IPT -P FORWARD DROP
$IPT -t nat -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P PREROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P POSTROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -N SERVICES
#drop spoofed packets
$IPT -A INPUT --in-interface ! lo --source 127.0.0.0/8 -j DROP
#limit ping requests
$IPT -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp -m limit --limit 1/second -j ACCEPT
#drop bogus packets
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP
iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state INVALID -j DROP
iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ACK,PSH PSH -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ACK,URG URG -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,RST FIN,RST -j DROP
$IPT -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,PSH,URG -j DROP
#allowed inputs
$IPT -A INPUT --in-interface lo -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A INPUT -j SERVICES
#allow responses
$IPT -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
#allow services
$IPT -A SERVICES -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -m iprange --src-range 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 -p tcp --dport 631 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A SERVICES -m iprange --src-range 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 -p udp --dport 631 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
$IPT -A FORWARD -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
### End Of Script ###
Wednesday, December 15, 2010
OpenKM 5.0 on Ubuntu 10.04
Required is the install of Sun Java JDK 1.6 on Ubuntu 10.04.
We are going to be installing Java with the help of apt-get so, as you can guess, we will be doing this from the command line. So fire up your favorite terminal window and get ready to work.
The first step is to add the necessary repositories to the /etc/apt/sources.list file. So open that file up with your favorite text editor and add the following line to the bottom of that file:
deb http://archive.canonical.com/ lucid partner
Now to update apt, issue the command:
$ sudo apt-get update
Once apt has completed its update, you are ready to install. The actual installation command is:
$ sudo aptitude install sun-java6-jdk
Next is we need to get the install files of OpenKM, download the the zip file OpenKM-5.0_JBoss-4.2.3.GA.zip from http://www.openkm.com/Download.htmlUnzip the file and using winscp (http://winscp.net/eng/download.php)
- copy the jboss-4.2.3.GA folder to the Ubuntu /opt directory.
To manually run OpenKM, first go to /opt/jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin directory and run chmod +x *.sh
Then type ./run.sh -b 0.0.0.0 and enter.
Point your favorite browser to http://
Autenticate to OpenKM using user "okmAdmin" with password "admin"
To Run OpenKM as a Service so that OpenKM will run after a reboot, go to the console of ubuntu
Run $ vi /etc/init.d/jboss
Insert the following lines to the vi editor:
#! /bin/sh
# /etc/init.d/jboss: Start and stop JBoss AS
ECHO=/bin/echo
TEST=/usr/bin/test
JBOSS_START_SCRIPT=/opt/jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/run.sh
JBOSS_STOP_SCRIPT=/opt/jboss-4.2.3.GA/bin/shutdown.sh
$TEST -x $JBOSS_START_SCRIPT || exit 0
$TEST -x $JBOSS_STOP_SCRIPT || exit 0
start() {
$ECHO -n "Starting JBoss"
sudo $JBOSS_START_SCRIPT -b 0.0.0.0 > /dev/null 2> /dev/null &
$ECHO "."
}
stop() {
$ECHO -n "Stopping JBoss"
sudo $JBOSS_STOP_SCRIPT -S > /dev/null &
$ECHO "."
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
sleep 30
start
;;
*)
$ECHO "Usage: jboss {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
#end of script
$ sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/jboss
$ sudo update-rc.d jboss defaults
Done. The OpenKM now runs as a service. You can start OpenKM with
$ sudo ./etc/init.d/jboss start
Last step is to update the database config file to prevent the repositories from being deleted.
$ vi /opt/jboss-4.2.3.GA/OpenKM.cfg
Change the line hibernate.hbm2ddl=create to hibernate.hbm2ddl=none
Note:
From OpenKM 5.x there's a property definition in OpenKM.cfg to create automatically database. Once the tables are created, change the hibernate.hbm2ddl property from create to none. Do it after first time running, in other case all repository it'll be deleted and created in next OpenKM starting
Thursday, October 28, 2010
MRTG On Ubuntu Server
So, let’s get started.
Download and Install
First, download and install MRTG using apt-get:
sudo apt-get install mrtg |
sudo updatedb && locate mrtg |
sudo mkdir /etc/mrtg && sudo mv /etc/mrtg.cfg /etc/mrtg |
Configure
MRTG includes a script called cfgmaker that will help us populate mrtg.cfg with the information obtained from your gateway/router. But before you run cfgmaker, you should set up the snmp community. This usually involves logging into your gateway/router and enabling SNMP. The default community will typically be “public.” If you change the default community to another name though, make note of it. Now, run the following command, substituting the SNMP community name, if you’ve changed it, and adding the IP address of your gateway/router:
sudo cfgmaker --output /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg public@your-router's-IP-address |
RunAsDaemon: Yes |
Interval: 5 |
Logdir: /var/log/ |
EnableIPv6: no |
Speaking of graphs, by default MRTG graphs grow to the left, so by adding the option “growright” the direction of the traffic visible in MRTG’s graphs flips causing the current time to be at the right edge of the graph and the history values to the left of it. We’ve also chosen the “bits” option, which means that the monitored traffic values obtained from your gateway/router are multiplied by 8 and displayed bits per second instead of bytes per second. Finally, we’ve given MRTG a directory to put its log file, and because many routers do not currently support SNMP over IPv6, we’ve shut that off.
Okay, now it’s time to create the web pages which display the MRTG graphs. Run the following command:
sudo indexmaker --output=/var/www/mrtg/index.html /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg |
Start
There’s something important to keep in mind when starting MRTG, and that is that MRTG requires the environmental variable “LANG” to be C in order to run properly. Since most Linux systems these days, including Ubuntu server, use UTF-8 (run echo $LANG to see what your system uses), let’s change LANG to C and start MRTG using the following command:
sudo env LANG=C /usr/bin/mrtg /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg |
Well, that’s it. Now point your browser to http://your-server-address/mrtg and you should see a page that resembles the following. You may have more or less graphs depending on the number interfaces reported by your gateway/router.
Okay, so now that we have MRTG installed, configured and running let’s move on and discuss how to keep it running.
Operate
Starting MRTG by hand is not ideal in the long run. So perhaps after you’ve done some tweaking on MRTG and are satisfied with your results, you can automate the process of running MRTG by creating a startup script in your system startup sequence. Here’s the script that I use:
##### START OF SCRIPT #####
#!/bin/bash
### START OF SCRIPT
MRTG="/usr/bin/mrtg"
CONFIG="/etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg"
PIDFILE="/etc/mrtg/mrtg.pid"
LOCKFILE="/etc/mrtg/mrtg"
OPTIONS="--daemon"
RETVAL=0
start() {
echo -n $"Enabling MRTG: "
rm -f ${LOCKFILE} 2> /dev/null
env LANG=C ${MRTG} --pid-file=${PIDFILE} --lock-file=${LOCKFILE} ${OPTIONS} ${CONFIG}
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Disabling MRTG: "
kill `cat ${PIDFILE}` && rm -f ${LOCKFILE}
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
restart() {
stop
start
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart|force-reload)
restart
;;
status)
if [ -f $LOCKFILE ]; then
echo $"MRTG is enabled."
RETVAL=0
else
echo $"MRTG is disabled."
RETVAL=3
fi
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|force-reload}"
exit 1
esac
exit $RETVAL
###### END OF SCRIPT #####
| |
chmod +x mrtg && sudo mv mrtg /etc/init.d/ |
sudo ln -s /etc/init.d/mrtg /etc/rc2.d/S99mrtg |
sudo ln -s /etc/init.d/mrtg /etc/rc2.d/K99mrtg |
sudo /etc/init.d/mrtg start |
Conclusion
This concludes the article on how to install and configure MRTG on Ubuntu server. As you can see, MRTG isn’t terribly complicated and proves to be a really nice open source package for monitoring and displaying traffic in and out your network from virtually anywhere you have a web browser. For a full list of all the configuration options and other information I encourage you to visit the MRTG web site.
References
http://oss.oetiker.ch/mrtg/doc/index.en.html
Wednesday, July 21, 2010
Install OTRS 2.4 on Ubuntu 10.04 LTS Server
There are only two steps to install OTRS.
Step 1: From the console as root, run:
root@srv1:~# apt-get install libapache2-mod-perl2-dev
Step 2: root@srv1:~# apt-get install otrs2
If you forget to do Step 1, you will encounter an error ...
"dpkg: error processing otrs2 (--configure):
subprocess post-installation script returned error exit status 1
Errors were encountered while processing:
otrs2
E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)"
Run the following to fix the error:
root@srv1:~# apt-get install libapache2-mod-perl2-dev
Then purge the otrs install:
root@srv1:~# apt-get purge otrs2
And finally install again otrs
root@srv1:~# apt-get install otrs2
Once the installation is completed, Login to the website of OTRS:
http://[ip address of OTRS Server]
Username: root@localhost
Password: root
Thursday, March 25, 2010
Getting Midnight Commander line drawing to work with PuTTY
When using Midnight Commander with the default settings of PuTTY connected to my Ubuntu Linux machine the line drawing characters are all messed up.
After some experimentation it turns out that to fix it all you have to do is change your character set in PuTTY to UTF-8 and the problem is fixed. To do this open up the PuTTY settings and go to Window->Translation->Received data assumed to be in which character set: and change it to UTF-8.
After making this change you might have to force a redraw of the mc screen to show the new line drawing characters:
Also not that some fonts might not have the line drawing characters available. The fonts I know work is Courier New and Lucida Console. To change your font go to Window->Appearance, Font settings and click the Change button.
For reference, I was using using Midnight Commander 4.6.2 running on Ubuntu 8.04 and using PuTTY 0.60
Monday, March 22, 2010
Open Source Systems
Cloud Database
Development Environment
Virtual Appliance:
Open Source Helpdesk Ticketing Systems
Sunday, March 7, 2010
Vmware Free Backup Utility
You can download the tool at http://www.veeam.com/vmware-esxi-fastscp.html
Tuesday, March 2, 2010
Cisco Graphical Network Simulator
To simulate a network, I came across a Graphical Network Simulator found at GNS3.net
There is a short tutorial on Youtube on how to setup GNS3 that can be found at
You will need Cisco IOS Images to run GNS3, that you can download at:
- http://sobek.su/Cisco/IOS/
- http://thepiratebay.org/torrent/4409592/Cisco.IOS.Monster.Collection.2008
Monday, March 1, 2010
Video Editing Tools
I got our on site video for our wedding last July 11, 2009 from NICE Print.
I was so eager to put the video on Youtube.
First I needed to convert the video. It was in DVD .vob format and I needed .mp4.
I downloaded WinX DVD Ripper. Awsome tool.
Second, I needed to edit the video to crop the dark margins on top and below the video. It was in widescreen format. I then downloaded iWisoft Free Video Editor
With these two tools you can rip your dvds and edit\crop them as you wish to put on youtube.
Tuesday, February 2, 2010
Video Security with ZoneMinder and Ubuntu
In this post I’ll provide you with a free-style guide on how to set up video security system that supports above mentioned features and is based on rather cheap webcams, free as beer software ZoneMinder and Ubuntu. I used Hardy Heron Ubuntu (8.04) for the installation but this guide should also work for 8.10 (Intrepid Ibex) and Jaunty Jackalope (9.04).
The webcam we played with is manufactured by Logitech and has model name “QuickCam Chat”. It’s USB 2.0 camera that allows to capture video with 352×288 quality and 30 frames per second. Actually it’s more than enough for home security appliance. Thanks to heaven this camera is supported by Ubuntu by default as it works well with gspca/spca5xx driver.
You can check your webcam Linux compatibility here (it’s highly recommended to look through this list before buying camera). If your one is supported and column “Support” in above mentioned list is green it’s time to install drivers. Ubuntu users should execute the following command to install it:
sudo aptitude install gspca-source -y
After it’s done, you should restart your computer or run sudo modprobe gspca in order to load newly installed driver (don’t forget to plug your webcam). To check if driver is loaded normally you can run dmesg and look for “gspca” related lines, like these ones:
[15808.524000] usbcore: registered new interface driver gspca
[15808.524000] /home/viper/gspcav1-20070508/gspca_core.c: gspca driver 01.00.18 registered
To check if your cam works okay with installed driver, there are two simple programs that can help you: xawtv and camorama both can be installed with apt-get or aptitude). Just after you run one of these programs you should get clean picture. If it’s not clean there is no reason to proceed with this manual but to get your cam working (Google helps in most cases).
The next step is to install ZoneMinder – a heart of our system. As it comes from developers’ site, it’s top Linux video camera security and surveillance solution.
" ZoneMinder is intended for use in single or multi-camera video security applications, including commercial or home CCTV, theft prevention and child or family member or home monitoring and other care scenarios. It supports capture, analysis, recording, and monitoring of video data coming from one or more video or network cameras attached to a Linux system."
Installation procedure of ZoneMinder is extremely simple with Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install zoneminder apache2 php5-mysql libapache2-mod-php5 mysql-server ffmpeg
if you use Dapper or Feisty I recommend you to read this.
Once apt-get installation is finished run the following commands:
sudo ln -s /etc/zm/apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf.d/zoneminder.conf
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 force-reload
At this point ZoneMinder is installed, and you can load it’s control panel with your favorite browser (I hope it’s Firefox ): http://127.0.0.1/zm/ (replace 127.0.0.1 with IP address of computer you’ve installed ZoneMinder to). You should see empty ZoneMinder Console Page. If you see it the next step is to configure ZoneMinder, if you don’t it’s time to ask Google to help you or pray for gurus of this forum
Click at the “Options” of ZoneMinder Console to configure it. Here are screenshots of two main tabs:
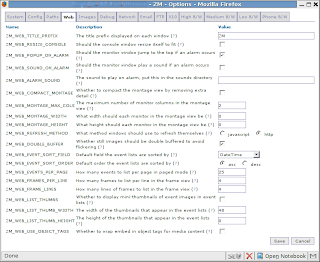
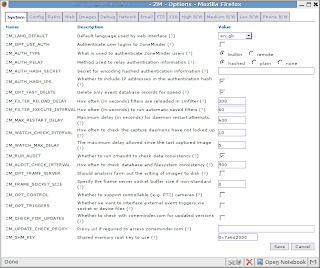
After you saved new settings by pressing “Save” button it’s necessary to apply them:
sudo /etc/init.d/zoneminder restart.
The next step is to create camera monitors. Click at “Add new monitor” and fill up suggested fields as it’s shown at the following pictures:
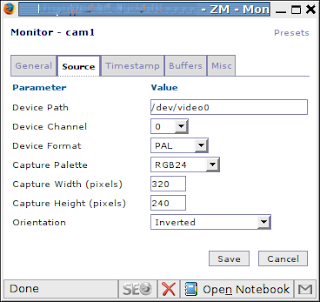
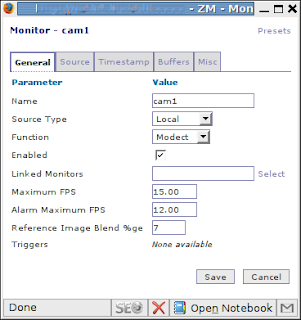
Don’t forget to set up function for newly added monitor (press appropriate link).
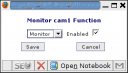
If everything is done properly after pressing at the name of Monitor you’ve added you should see the picture like this one:
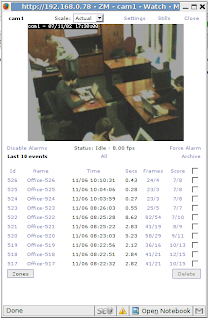
In case you have multiple cameras you should add more ZoneMinder monitors. That’s it, system is up and running.
By the way ZoneMinder has a lot of useful functions and is well documented, so I hope it won’t be difficult to set up certain feature.
Monday, January 25, 2010
How to Regenerate Reports in Untangle
You can regenerate a report from the terminal.
"/usr/lib/python2.5/reports/process.py"
For Untangle 6.X.X
You can regenerate a report from the terminal.
"/usr/share/untangle/reports/update-reports"
Sunday, January 10, 2010
Install MediaWiki on Ubuntu
Install the package:
sudo apt-get install mediawiki
sudo apt-get install imagemagick mediawiki-math php5-gd
sudo nano /etc/mediawiki/apache.conf
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
How to install the packages from the EPEL software repository
What is EPEL
Why we use EPEL repository?
- Provides lots of open source packages to install via Yum.
- Epel repo is 100% open source and free to use.
- It does not provide any core duplicate packages and no compatibility issues.
- All epel packages are maintained by Fedora repo.
How To Enable EPEL Repository in RHEL/CentOS 7/6/5?
RHEL/CentOS 7 64 Bit
## RHEL/CentOS 7 64-Bit ##
# wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-2.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-7-2.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 6 32-64 Bit
## RHEL/CentOS 6 32-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
## RHEL/CentOS 6 64-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 5 32-64 Bit
## RHEL/CentOS 5 32-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
## RHEL/CentOS 5 64-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/x86_64/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 4 32-64 Bit
## RHEL/CentOS 4 32-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/4/i386/epel-release-4-10.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-4-10.noarch.rpm
## RHEL/CentOS 4 64-Bit ##
# wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/4/x86_64/epel-release-4-10.noarch.rpm
# rpm -ivh epel-release-4-10.noarch.rpm
How Do I Verify EPEL Repo?
# yum repolist
Sample Output
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, priorities
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos.aol.in
* epel: ftp.cuhk.edu.hk
* extras: centos.aol.in
* rpmforge: be.mirror.eurid.eu
* updates: centos.aol.in
Reducing CentOS-5 Testing to included packages only
Finished
1469 packages excluded due to repository priority protections
repo id repo name status
base CentOS-5 - Base 2,718+7
epel Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 5 - i386 4,320+1,408
extras CentOS-5 - Extras 229+53
rpmforge Red Hat Enterprise 5 - RPMforge.net - dag 11,251
repolist: 19,075
How Do I Use EPEL Repo?
# yum --enablerepo=epel info zabbix
Sample Output
Available Packages
Name : zabbix
Arch : i386
Version : 1.4.7
Release : 1.el5
Size : 1.7 M
Repo : epel
Summary : Open-source monitoring solution for your IT infrastructure
URL : http://www.zabbix.com/
License : GPL
Description: ZABBIX is software that monitors numerous parameters of a network.
Let’s install Zabbix package using epel repo option –enablerepo=epel switch.
# yum --enablerepo=epel install zabbix
Note: The epel configuration file is located under /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.
Thursday, January 7, 2010
Block Yahoo Mail Chat Feature in Untangle
http://help.yahoo.com/l/us/yahoo/mail/yahoomail/chat/chat-23.html;_ylt=AuRtahSGRrYxeHLwwMzZoztq5yN4
Just create a rule for each of the websites to be blocked under the webfilter:
Webfilter --> Block Lists (Sites) --> Add -->
Site:webcs.msg.yahoo.com
Check Block & Log
Description: "whatever you like"
Second Rule
Site:httpcs.msg.yahoo.com
Check Block & Log
Description: "whatever you like"
I have tried and I keep being offline can not connect at all.
Wednesday, January 6, 2010
Running VMware vSphere Client on Windows 7
One of the very few inconveniences I have found with it, and this is not an bug or problem with Windows 7 itself, is the inability to run the VMware vSphere Client.
UPDATE: Good News – This issue has now been resolved in VMware ESX/ESXi 4.0 Update 1 (U1).
When attempting to run the client the following errors are received and you are unable to proceed any further:
“Error parsing the server “
“The type initializer for ‘VirtualInfrastructure.Utils.HttpWebRequestProxy’ threw an exception.”
Luckily there have been a few good VMware forum posts such as this one by ftubio which outlines how to successfully run the vSphere Client under Windows 7.
If you are running the x64 version of Windows 7 you will notice that any reference to the ‘Program Files’ will have an ‘(x86)’ at the end of it. If you are running the x86 version of Windows 7 then ignore the ‘(x86)’ portion of the directory path (ie: C:\Program Files (x86) –> C:\Program Files).
Follow these 4 basic steps and you’ll be up and running in no time!
Step 1.
Download this DLL called system.dll
*Note: This DLL is usually found in the %SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\ directory of a non Windows 7 PC with .NET v3.5 SP1 installed.
Step 2.
Once downloaded install it in the “C:\Program Files\VMware\Infrastructure\Virtual Infrastructure Client\Launcher\Lib” directory. If the ‘lib’ directory doesn’t exist then create it and drop the dll file into it.
Step 3.
Next edit the “VpxClient.exe.config” file which can be found in the “C:\Program Files\VMware\Infrastructure\Virtual Infrastructure Client\Launcher” directory and add the following three lines to it right below . Then save the changes.
Step 4.
From the Windows 7 ‘System Properties’ click the ‘Advanced’ tab and then the ‘Environment Variables’ button as we want to add a new ‘System’ variable.
Create a new ‘System’ variable called ‘DEVPATH’ and assign the following variable value:
C:\Program Files\VMware\Infrastructure\Virtual Infrastructure Client\Launcher\Lib
You are now ready to start using the VMware vSphere Client on your Windows 7 machine! Some people have reported having to run the client as an ‘Administrator’ so if you are having difficulties it may pay to try this – I luckily didn’t experience this problem. Also you will likely have to reboot your machine (or restart the explorer.exe process) for your new path information to come into effect.
